Navigating the Energy Grid: A Deep Dive into the US Electrical Grid Map
Associated Articles: Navigating the Energy Grid: A Deep Dive into the US Electrical Grid Map
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Navigating the Energy Grid: A Deep Dive into the US Electrical Grid Map. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Energy Grid: A Deep Dive into the US Electrical Grid Map
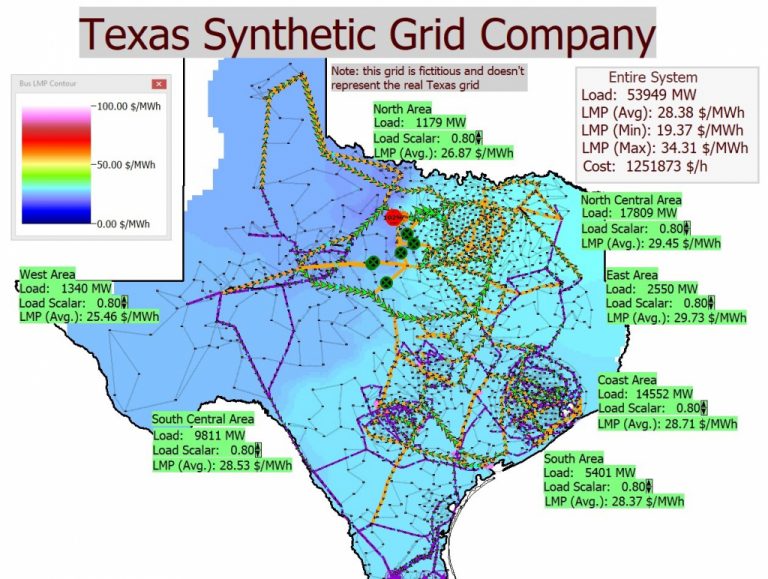
The US’ electrical grid is a colossal, interwoven community of energy vegetation, transmission strains, substations, and distribution techniques, delivering electrical energy to almost each nook of the nation. Visualizing this intricate infrastructure is essential for understanding its complexities, vulnerabilities, and future wants. This text delves into the importance of US electrical grid maps, exploring their numerous types, the info they signify, their purposes, and the challenges in creating and sustaining correct, complete representations.
Past Easy Strains: The Layers of a Complete Grid Map
A easy map depicting energy strains might sound ample at first look. Nevertheless, a very complete US electrical grid map must embody way over simply the visible illustration of transmission strains. It is a multi-layered system revealing essential details about:
-
Era Sources: The map ought to clearly determine the situation and capability of varied energy vegetation, differentiating between fossil fuel-based vegetation (coal, pure fuel, oil), nuclear energy vegetation, renewable vitality sources (photo voltaic, wind, hydro, geothermal), and different sources. This enables for evaluation of vitality combine, regional dependence on particular assets, and potential vulnerabilities as a consequence of reliance on a single supply.
-
Transmission Strains: These high-voltage strains kind the spine of the grid, transporting electrical energy over lengthy distances. The map ought to point out voltage ranges (e.g., 500 kV, 230 kV, 115 kV), line capability, possession (usually a mixture of personal and public entities), and the age and situation of the infrastructure. This reveals bottlenecks, potential weak factors, and areas needing upgrades.
-
Substations: These essential parts rework high-voltage electrical energy from transmission strains into decrease voltages appropriate for distribution to houses and companies. The map ought to present their location, capability, and connectivity to each transmission and distribution networks. Understanding substation capability is vital for managing peak demand and stopping outages.
-
Distribution Networks: These lower-voltage strains ship electrical energy from substations to particular person customers. Whereas usually not proven intimately on large-scale maps, their inclusion is crucial for localized evaluation of grid efficiency and resilience. The density of distribution networks varies considerably throughout areas, reflecting inhabitants density and vitality consumption patterns.
-
Management Programs: The trendy grid depends closely on subtle management techniques that monitor and handle the circulate of electrical energy in real-time. Whereas in a roundabout way visible, understanding the situation of management facilities and their communication networks is essential for assessing the grid’s total operational reliability.
-
Knowledge Overlay: A very highly effective grid map integrates information past bodily infrastructure. This may embody real-time information on electrical energy technology, consumption, and transmission flows; climate information impacting renewable vitality manufacturing; and knowledge on deliberate upgrades or upkeep actions. This dynamic layer enhances the map’s analytical capabilities.
Purposes of US Electrical Grid Maps
The purposes of correct and detailed US electrical grid maps are huge and span numerous sectors:
-
Grid Planning and Operations: Utilities use grid maps to plan for future infrastructure wants, optimize energy circulate, handle peak demand, and stop outages. Actual-time information overlays allow proactive response to altering situations and potential grid emergencies.
-
Renewable Vitality Integration: Maps assist determine optimum places for brand new renewable vitality tasks, contemplating components like transmission capability, proximity to load facilities, and potential grid impacts. Understanding current infrastructure is essential for seamless integration of intermittent renewable sources.
-
Grid Safety and Resilience: Maps help in figuring out vulnerabilities to cyberattacks, bodily threats, and excessive climate occasions. This enables for proactive safety measures and improvement of methods to boost grid resilience.
-
Market Evaluation and Policymaking: Grid maps present helpful information for market individuals, regulators, and policymakers to research electrical energy markets, assess the influence of insurance policies on grid improvement, and make knowledgeable selections about vitality infrastructure investments.
-
Public Consciousness and Training: Simplified variations of grid maps can assist educate the general public in regards to the complexities of the electrical energy system and the significance of grid modernization. This fosters higher understanding and help for investments in grid infrastructure.
-
Emergency Response: Throughout energy outages or pure disasters, grid maps are important instruments for emergency responders to evaluate the extent of harm, prioritize restoration efforts, and coordinate assets successfully.
Challenges in Creating and Sustaining Correct Grid Maps
Regardless of their essential function, creating and sustaining correct US electrical grid maps presents vital challenges:
-
Knowledge Availability and Standardization: Knowledge on grid infrastructure is usually scattered throughout numerous sources, with inconsistent codecs and ranges of element. Lack of standardization hinders the creation of complete, built-in maps.
-
Knowledge Privateness and Safety: Grid information can comprise delicate details about infrastructure vulnerabilities and operational methods. Defending this information from unauthorized entry is paramount.
-
Map Scale and Decision: Balancing the necessity for detailed data with the power to visualise your entire nationwide grid at a manageable scale is a fancy process. Totally different maps are wanted for various functions, starting from extremely detailed native maps to broad nationwide overviews.
-
Dynamic Nature of the Grid: The grid is continually evolving, with new technology sources being added, transmission strains being upgraded, and demand patterns shifting. Maintaining maps up-to-date requires steady information updates and upkeep.
-
Value and Sources: Creating and sustaining complete grid maps requires vital funding in information acquisition, software program improvement, and personnel. This generally is a barrier for smaller utilities and organizations.
The Way forward for US Electrical Grid Mapping
The way forward for US electrical grid mapping lies in leveraging developments in information analytics, geographic data techniques (GIS), and synthetic intelligence (AI). These applied sciences can improve the accuracy, element, and dynamism of grid maps, enabling simpler grid planning, operation, and administration. The event of open information initiatives and standardized information codecs can even be essential for fostering collaboration and bettering information accessibility.
Moreover, the mixing of real-time information from good meters, sensors, and different grid-connected units will present a extra granular and dynamic view of grid efficiency. This may allow predictive analytics to anticipate potential issues and optimize grid operations proactively.
The event of interactive, three-dimensional grid maps will present a extra intuitive and immersive understanding of the complicated infrastructure. This may help in communication with stakeholders, facilitate public engagement, and improve decision-making processes.
In conclusion, the US electrical grid map is way over a easy visible illustration; it is a vital instrument for understanding, managing, and modernizing our nation’s energy infrastructure. Overcoming the challenges related to information assortment, standardization, and upkeep is essential for realizing the complete potential of grid mapping and making certain a dependable, resilient, and sustainable vitality future. The continued funding in know-how and collaborative efforts might be key to growing more and more subtle and efficient grid maps that serve the wants of utilities, policymakers, and the general public alike.


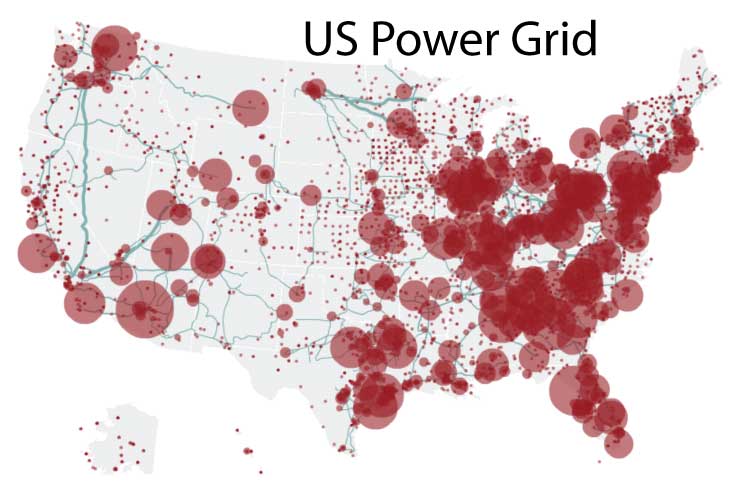



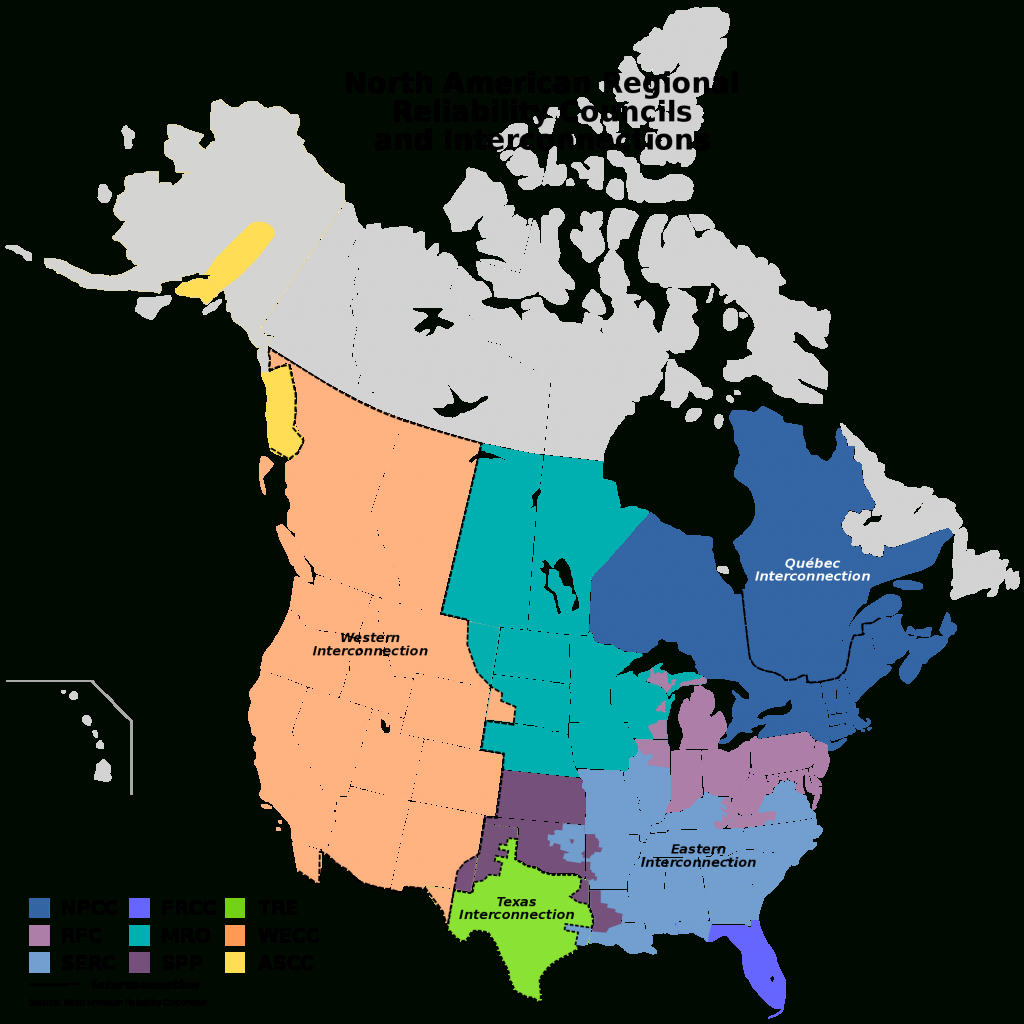
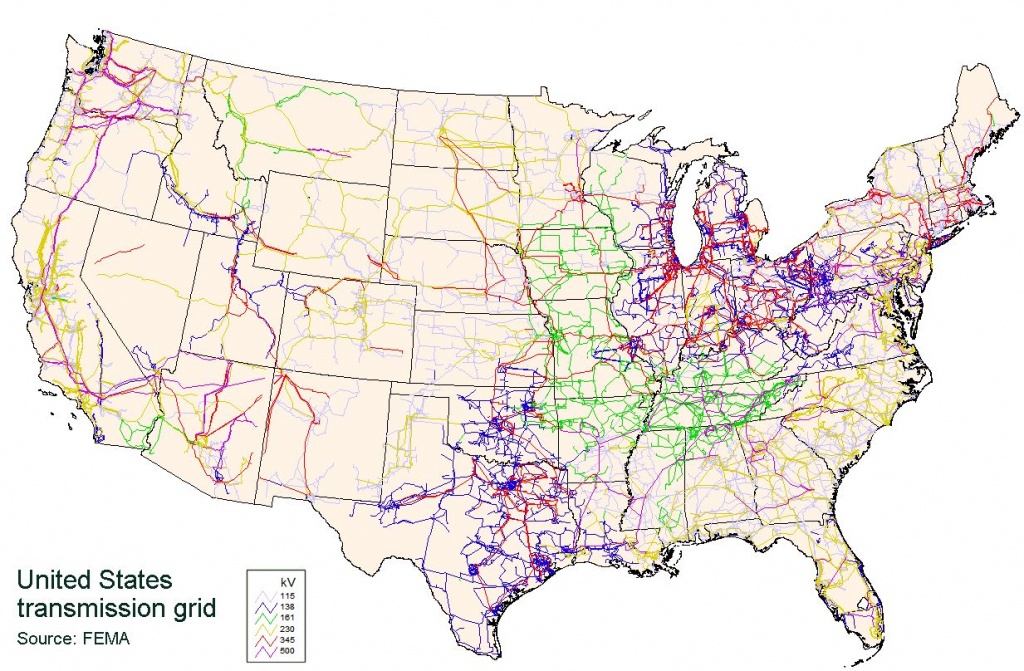
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Navigating the Energy Grid: A Deep Dive into the US Electrical Grid Map. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!